Decoding the Differences: Nutritionist vs Dietician
Introduction:
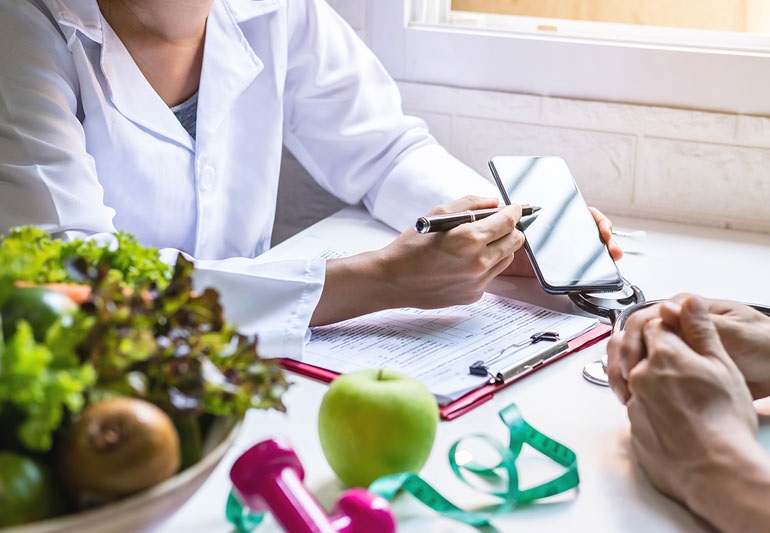
In health and wellness, “nutritionist” and “dietician” are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion among individuals seeking professional dietary advice. While both roles involve guiding individuals toward better nutrition, there are distinct differences between nutritionists and dietitians. This blog post will explore these disparities to help you make informed dietary choices.
Key Differences:
- Education and Training:
- Nutritionist: Nutritionists typically acquire knowledge through various educational paths, including online courses, workshops, or certifications. However, there is no standardized educational requirement for the title.
- Dietitian: On the other hand, dietitians undergo more rigorous education and training. They often hold at least a bachelor’s degree in dietetics or a related field and must complete a supervised internship. Many dietitians also pursue advanced degrees.
- Credentialing:
- T assesses the qualifications of a nutritionist.
- Dietitian: Dietitians are usually required to obtain professional credentials, such as becoming a Registered Dietitian (RD) or a Licensed Dietitian (LD), depending on the country or state—standardized level of education and expertise.
- Scope of Practice:
- Nutritionist: Nutritionists often focus on general nutrition advice, lifestyle changes, and wellness. However, their recommendations may need more specificity for medical conditions or complex dietary needs.
- Dietitian: Dietitians have a broader scope of practice. They are trained to provide therapeutic nutrition interventions, manage medical conditions, and work in healthcare settings to create specialized diet plans.
People Also Ask (FAQs):
Q1: Can a nutritionist give personalized dietary advice?
- Answer: While nutritionists can provide general advice, dietitians are better equipped to offer personalized dietary recommendations based on individual health needs.
Q2: Are dietitians more expensive than nutritionists?
- Answer: The cost may vary, but dietitians’ additional education and training can sometimes result in higher fees. However, their expertise often justifies the investment in managing health and nutrition effectively.
Q3: Can a nutritionist work in a hospital?
- Answer: In many cases, dietitians are preferred in hospital settings due to their comprehensive training and ability to handle medical conditions. However, some nutritionists with specific qualifications may also work in healthcare.
Q4: How can I verify if a nutritionist is credible?
- Answer: Look for certifications from reputable organizations and check for relevant education and experience. Be cautious of unregulated titles and consult a registered dietitian for more reliable advice.
For more detailed insights into the distinctions between nutritionists and dietitians, you can visit FitBudd.
Conclusion:
Understanding the differences between nutritionists and dietitians is crucial when seeking professional dietary guidance. Whether you opt for a nutritionist or a dietitian, making an informed decision will empower you to achieve your health and wellness goals. For further exploration of this topic, visit FitBudd.